SparkyChem
Member level 3

- Joined
- Apr 22, 2010
- Messages
- 57
- Helped
- 0
- Reputation
- 0
- Reaction score
- 0
- Trophy points
- 1,286
- Location
- Lima, Peru
- Activity points
- 2,084
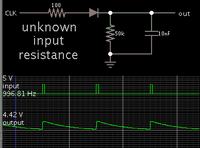
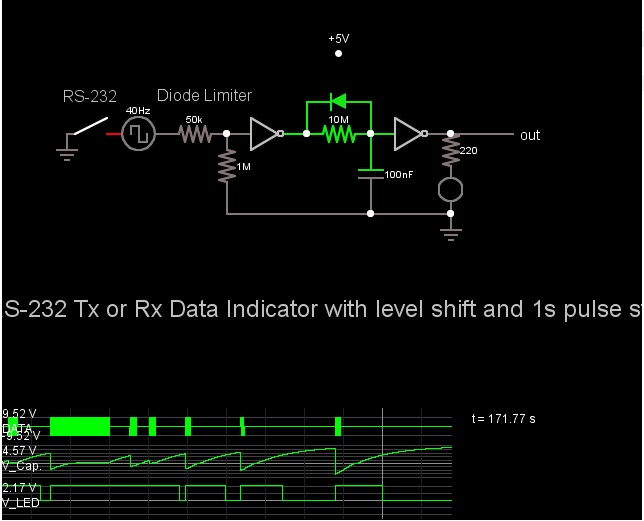
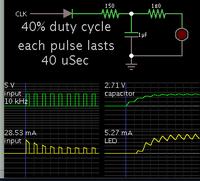
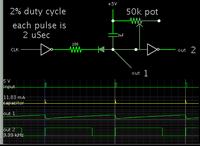
Hello, i need help on designing a proper circuit for adding status leds using a MAX232 when connected to a PIC. i tried the usual setting tying leds from the TX and RX from the uC but the problem is that they dont lid correctly, i've been told that using a pulse stretcher would be a more efficient solution to this so i could see the bits more properly when they are being transmitted during serial communication. Can somebody would share to me a simple but effective CMOS 4000 series pulse stretcher that i can use to do this?. Thanks in advance.