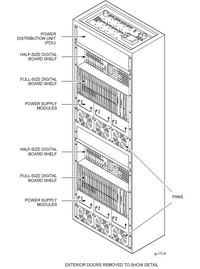
Aya2002
Advanced Member level 4
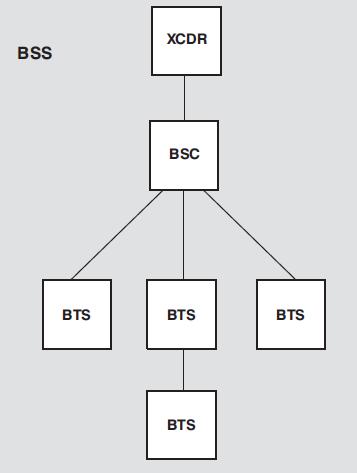
ss7 role in gsm network
you forget the XCDR
Added after 19 minutes:
GSM Network Components
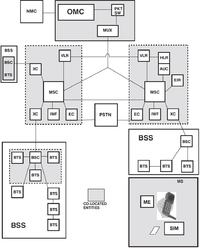
Now: GSM Terrestrial Interfaces
The terrestrial interfaces comprise all the connections between the GSM system entities, apart from the Um, or air interface. They are represented on the diagram opposite by the lines that connect the various entities together. The GSM terrestrial interfaces and message-transport mediums all conform to ITU-TSS
specifications widely used throughout the world. As we stated previously, it is from this use of standardized interfaces that the flexibility of GSM largely derives. The terrestrial interfaces transport the traffic across the system and allow the passage of the thousands of data messages necessary to make the system function. They transport the data for software downloads and uploads, the collection of statistical information and the implementation of operations and maintenance commands.
The standard interfaces used are as follows:
* 2 Mbit/s.
* Signalling System ITU-TSS #7 (“C7” or ‘‘SS#7”).
* X.25 (packet switched data); (LAPB).
* A bis using the LAPD protocol (Link Access Procedure “D”).
Whatever the interfaces and whatever their function, they will often share a common physical bearer (cable) between two points, for example, the MSC and a BSS.
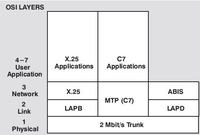
ITU-TS Signalling System #7
The diagram opposite illustrates the use of C7 in the GSM system; carrying signalling and control information between most major entities, and to and from the PSTN. The following message protocols, which are part of C7, are used to communicate between the different GSM network entities:
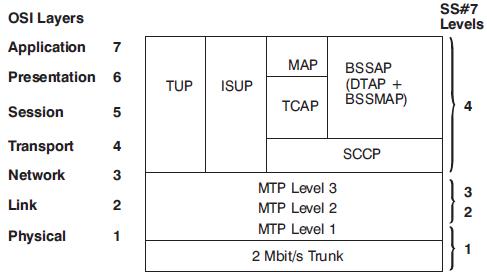
* Interfacing the PSTN, the MSC performs call signalling functions using the
Telephone User Part (TUP), or interfacing the ISDN, the ISDN User Part (ISUP).
* Between the MSC and the BSC, the Base Station System Management
Application Part (BSSMAP) is used. The Direct Transfer Application Part (DTAP)
is used to send messages between the MSC and the mobile (MS). MAP is used
between the MSC and the VLR, EIR, and HLR.
Acronyms:
BSSAP Base Station System Application Part
BSSMAP Base Station System Management Application Part
DTAP Direct Transfer Application Part
ISUP ISDN User Part
MAP Mobile Application Part
SCCP Signalling Connection Control Part
TUP Telephone User Part
TCAP Transaction Capabilities Application Part
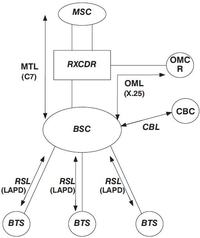
BSC Connections
Regards
leekk8 said:Sharing some info about SS7:
All the submodules in SS7 protocol stack:
- MTP1
- MTP2
- MTP3
- SCCP
- ISUP
- TUP
- SNM
- SNT
- MAP
- INAP/CAP
- TCAP
Added after 1 minutes:
Sharing info about GSM:
All the elements in GSM network:
- BTS
- BSC
- MSC
- VLR
- HLR
- AUC
you forget the XCDR
Added after 19 minutes:
GSM Network Components

Now: GSM Terrestrial Interfaces
The terrestrial interfaces comprise all the connections between the GSM system entities, apart from the Um, or air interface. They are represented on the diagram opposite by the lines that connect the various entities together. The GSM terrestrial interfaces and message-transport mediums all conform to ITU-TSS
specifications widely used throughout the world. As we stated previously, it is from this use of standardized interfaces that the flexibility of GSM largely derives. The terrestrial interfaces transport the traffic across the system and allow the passage of the thousands of data messages necessary to make the system function. They transport the data for software downloads and uploads, the collection of statistical information and the implementation of operations and maintenance commands.
The standard interfaces used are as follows:
* 2 Mbit/s.
* Signalling System ITU-TSS #7 (“C7” or ‘‘SS#7”).
* X.25 (packet switched data); (LAPB).
* A bis using the LAPD protocol (Link Access Procedure “D”).
Whatever the interfaces and whatever their function, they will often share a common physical bearer (cable) between two points, for example, the MSC and a BSS.

ITU-TS Signalling System #7
The diagram opposite illustrates the use of C7 in the GSM system; carrying signalling and control information between most major entities, and to and from the PSTN. The following message protocols, which are part of C7, are used to communicate between the different GSM network entities:

* Interfacing the PSTN, the MSC performs call signalling functions using the
Telephone User Part (TUP), or interfacing the ISDN, the ISDN User Part (ISUP).
* Between the MSC and the BSC, the Base Station System Management
Application Part (BSSMAP) is used. The Direct Transfer Application Part (DTAP)
is used to send messages between the MSC and the mobile (MS). MAP is used
between the MSC and the VLR, EIR, and HLR.
Acronyms:
BSSAP Base Station System Application Part
BSSMAP Base Station System Management Application Part
DTAP Direct Transfer Application Part
ISUP ISDN User Part
MAP Mobile Application Part
SCCP Signalling Connection Control Part
TUP Telephone User Part
TCAP Transaction Capabilities Application Part
BSC Connections

Regards