baby_1
Advanced Member level 1
Hello
what is difference between RADIATION INTENSITY power density?
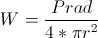
Balanis Antenna Theory:
2.4 RADIATION INTENSITY
Radiation intensity ina givendirectionis defined as “the power radiated from an
antenna per unit solid angle.” The radiation intensity is a far-field parameter, and
it can be obtained by simply multiplying the radiation density by the square of the
distance.
what is difference between RADIATION INTENSITY power density?
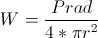
Balanis Antenna Theory:
2.4 RADIATION INTENSITY
Radiation intensity ina givendirectionis defined as “the power radiated from an
antenna per unit solid angle.” The radiation intensity is a far-field parameter, and
it can be obtained by simply multiplying the radiation density by the square of the
distance.
Last edited: