snishanth512
Full Member level 3
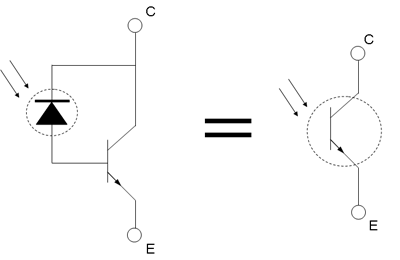
Please explain with diagrams....
I am searching for IR LED of 940nm for my project.....
I am searching for IR LED of 940nm for my project.....
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
Please explain with diagrams....
I am searching for IR LED of 940nm for my project.....
Why do we use resistor R2 in the diagram(given in the above reply)?
Why do we use resistor R2 in the diagram(given in the above reply)?