Vlad.
Full Member level 3
- Joined
- Jun 4, 2012
- Messages
- 179
- Helped
- 3
- Reputation
- 6
- Reaction score
- 4
- Trophy points
- 1,298
- Location
- Bucharest/Romania
- Activity points
- 2,568
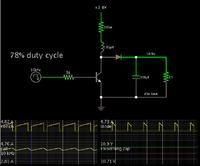
I design a boost converter with uc3843+irf3205 to make 20v adjustable from 12v. now i have the efficeny about 82%, how can i make it up to 90%? who know some tricks for that?