sameerdhiman
Member level 5
Hi,
Can somebody give me the mathematical formula for the following circuit.
Where R1≠R2≠R3≠R4, R5 is variable. Calculate Vout for any V1 value.
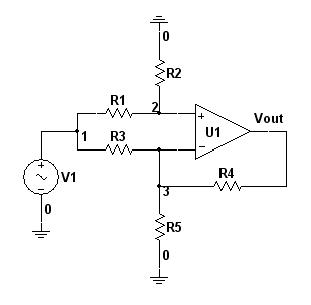
Can somebody give me the mathematical formula for the following circuit.
Where R1≠R2≠R3≠R4, R5 is variable. Calculate Vout for any V1 value.
